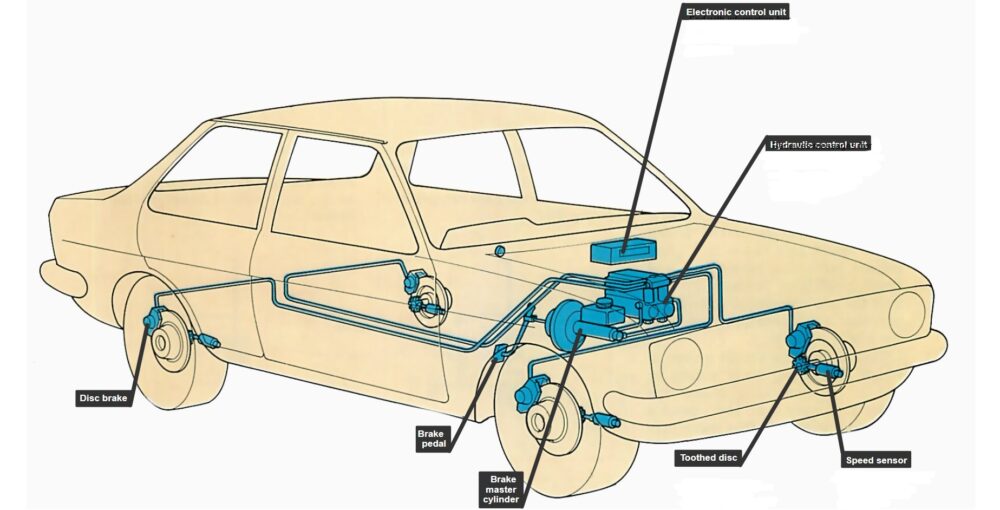
ABS stands for Anti-Lock Braking System and as the name implies it prevents the wheels from locking up in the case of an emergency. This allows the driver to maintain control of the vehicle and steer away from the obstacle. ABS also helps the car to come to an early stop as compared to non-ABS vehicles.
Types of ABS
There are two types of ABS, two-wheel and four-wheel. Two-wheel ABS is mostly used in light trucks and rear-wheel-drive vehicles. Two-wheel ABS prevents the rear wheels from locking up but the front wheels still get locked and the vehicle moves in a straight line, but with the right amount of pressure on the brake pedal the driver can steer the vehicle.
Four-wheel ABS is found in some light trucks and in most cars. Four-wheels ABS prevents the locking of both front and rear wheels and prohibits the wheels from locking up while simultaneously allowing the driver to maintain directional stability.
How Does the ABS Work
The vehicle’s onboard computer uses a microprocessor called the Anti-Lock Brake Computer to monitor the speed of your vehicle with a speed sensor. Whenever the driver applies the brakes the onboard computer compares the speed of rotation of each tire and triggers electronic solenoids to encourage or discourage hydraulic pressure to each wheel. This is done in order to match the speed of rotation of each tire.
You can feel the brake pedal pulsing beneath your foot when the ABS becomes active. Keep in mind that in ABS vehicles you have to keep continuous pressure on the brake. If you ease on the brake pedal the ABS will disengage and the vehicle will skid.
This is the main difference between ABS and Non-ABS vehicles as in ABS vehicles the driver needs to apply constant pressure on the brake pedal and drivers with non-ABS vehicles practice cadence braking. Also, make sure to check the instrument panel as an amber-colored ABS check light will come on if it doesn’t work. Don’t worry the driver will still have normal braking.
Other Forms of Braking Assist
There are two other forms of braking assists that are coupled with ABS, namely, Brake Assist and Electronic Brakeforce Distribution (EBD).
Brake Assist
The brake assist keeps a track of your braking habit and as soon as it detects that you are pressing on the brake with more than usual force it boosts the power of the brake in order for you to come to an early stop and as soon as you lift your foot off the brake pedal the system lets go of the brakes and you can resume normal driving. It is also called the “pre-collision package”.
Electronic Brakeforce Distribution
EBD is another useful function that monitors the weight distribution of each vehicle and determines how much braking force needs to be applied at each wheel independently. This is often offered in luxury and Sports Utility Vehicles (SUVs). If an equal amount of brake force is applied to each wheel and the weight is unequally distributed the vehicle will pull to one side and skid. This system ensures that a proportionate amount of braking force is distributed to bring the car to a stop without skidding.