The human body is built for motion.
Muat Dalkilinç for TED-Ed explains that we have over 360 joints and around 70 skeletal muscles. Our skin is elastic and molds to movement, our nerve cells benefit from moving around, blood flow depends upon motion and we have the ability to stand straight against gravity.
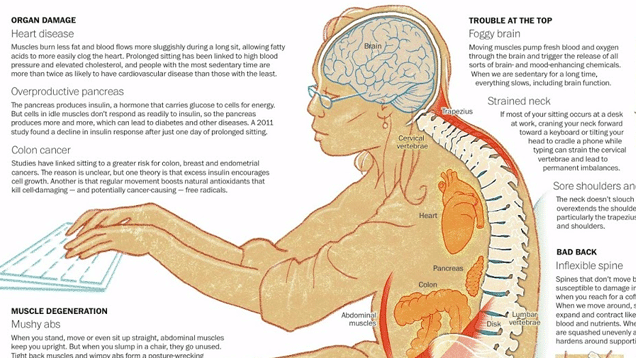
So what becomes of our bodies when we sit down for longer periods of time? This graphic from the Washington Post explains it:
Bad Posture
The first impact of sitting down for extended time periods is on our spine. The human spine is a structure of bones and cartilage discs. Slumped shoulders and curved backs cause unnecessary pressure on these discs, and results in wear and tear of spinal cord muscles over time.
This also causes our chest cavity to shrink, which prevents our lungs from doing their best and limits the amount of oxygen. This also gives us weak abdominal muscles, which go unused in long periods of bad posture.
Trouble at the top
Slouching for extended time periods gives sore shoulders. It also strains neck muscles and impacts the cervical vertebrae. This frequently results in a headache at the back of the skull known as a ‘tension headache’.
The other dangers of prolonged inactivity are more serious. Poor posture impacts oxygen in lungs and decreased blood flow makes things worse. The human brain cannot function without oxygenated blood supplies. This means that concentration levels and productivity decline. Staying active also releases endorphin, an important chemical for a happy mood without which stress levels climb.
Muscle Degeneration
Our body muscles make up most of the delicate tissue beneath our skin. Because they are designed for movement, sitting down for long hours causes degeneration. This results in numbness, swelling and weak muscles.
Risk of Disease
Staying seated temporarily deactivates the production of the lipoprotein lipase, an enzyme which helps the breakdown of fat cells. It also prevents the blood from properly reacting to insulin production. Insulin helps transport glucose to cells for energy production, so an idle person has a greater risk of heart disease and obesity.
Research further proves that prolonged inactivity leads to kidney and liver problems and in some cases, even cancer. Inactivity causes 9% of the world’s premature deaths every year.
Solutions
Contemporary lifestyle revolves around long hours of being chained to desks and schools and offices, but the world is changing. Schools in Finland have adopted regular physical activity breaks during study hours, and the trend is slowly spreading in the rest of the world.
A simple solution is to reward your body with a short walk every half hour.


























Thanks
going for all prayers is best solution to cope with excessive sitting
GREAT!
At least credit the author of the cover picture. ASAP Science!