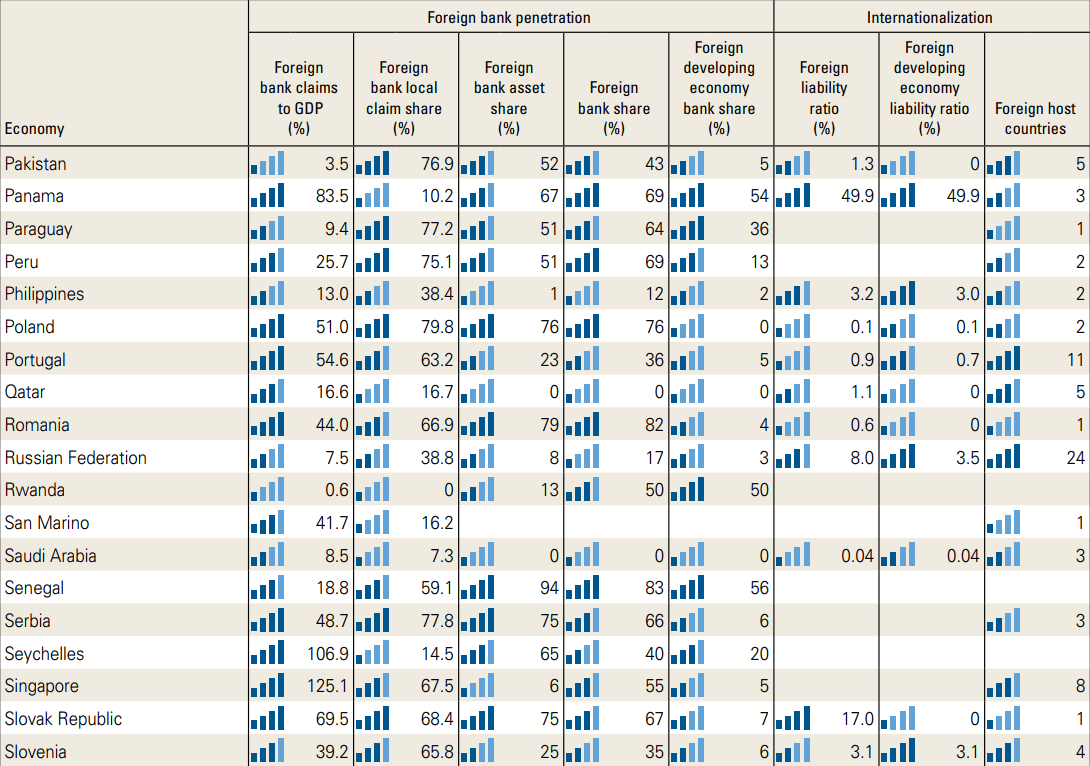
The penetration of foreign banks in Pakistan is getting low with minimal contribution in local banking industry and the overall economy.
According to a study conducted by the World Bank Group, “Bankers without Borders”, the share of foreign banks to GDP stands at 3.5 percent whilst private credit by deposit to GDP stands at 15.4 percent.
Private credit by deposit-money banks to GDP (%) measures the domestic private credit to the real-sector by deposit-money banks as a percentage of local currency GDP.
In the wake of the global financial crisis, the globalization trend has been partially reversed as multinational banks from developed countries have scaled back their international operations, coinciding with a general backlash against globalization.
Foreign banks have scaled down their operations and businesses in Pakistan mainly due to their policies defined by headquarters: to shrink their operations in small and struggling markets.
Banks closing down or shortening of their operations included Royal Bank of Scotland, Citibank that sold out its consumers banking portfolio to Habib Bank Limited and restricted to corporate banking.
Other foreign banks operating in Pakistan are Deutsche Bank, Samba Bank, Industrial and Commercial Bank of China, Bank of Tokyo and the newly established Bank of China.
Standard Chartered Bank is operating in profit but it has merged its subsidiaries—Standard Chartered Leasing Company and Standard Chartered Modaraba with Orix Leasing.
International banks are involved in two major types of international activities: cross-border flows, and foreign participation in domestic banking systems through brick-and-mortar operations.
Trade-in financial services mostly take place through cross-border operations of a bank, in-lending, deposit taking, or insurance; and provision of these services through a foreign bank’s presence, which can take the form of a subsidiary or a branch in a foreign country.
International banking activities may contribute to faster growth, greater welfare, and enduring stability in two important ways:
- First, by bringing much-needed capital, expertise, and new technologies, thereby leading to more competitive banking systems.
- Second, by enabling risk sharing and diversification, thereby smoothing out the effects of domestic shocks.





















Panama 83.50?