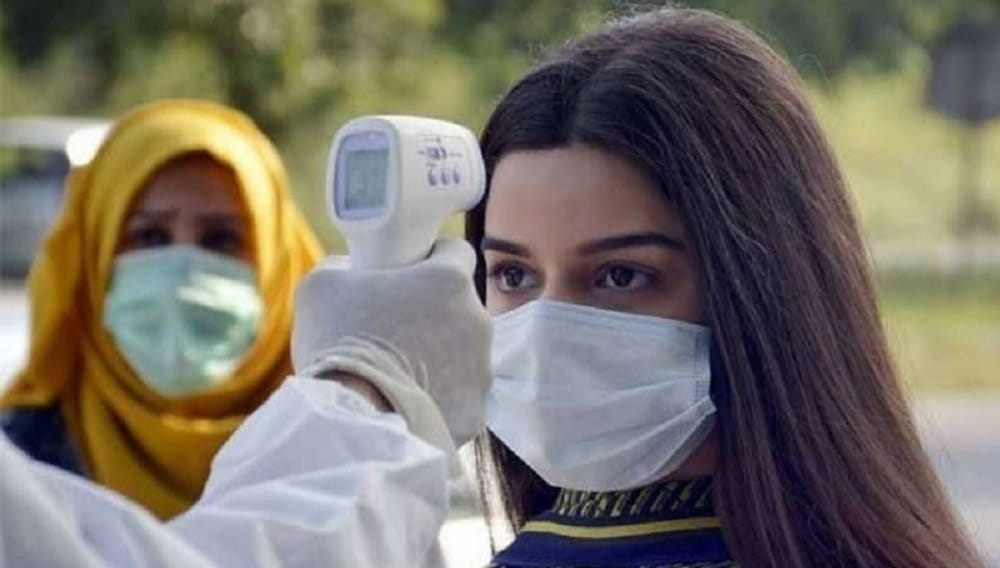
The National Institute of Health (NIH) has issued an advisory aimed at tackling the prevention and control of the JN.1 sub-variant of COVID-19.
The JN.1 sub-variant has been designated as a variant of concern (VOC), stemming from the BA.2.86 sub-variant of the omicron variant. This sub-variant has rapidly spread across various countries and is exhibiting a significant global surge.
NIH’s Call for Improved Preparedness
The Center for Disease Control at NIH has issued this advisory to support health authorities in enhancing preparedness measures for the prevention and control of this particular sub-variant.
Low Morbidity and Mortality Rates
The advisory highlights that the JN.1 sub-variant is unlikely to trigger a scenario similar to the initial phases of the pandemic.
Current statistics indicate low morbidity and mortality rates, despite its swift displacement of other sub-variants. Additionally, its transmissibility is anticipated to be high.
Symptoms of JN.1 Infection
Similar to other sub-variants, JN.1 infection manifests with symptoms such as cough, sore throat, congestion, runny nose, sneezing, fatigue, headache, muscle aches, and altered sense of smell.
The document emphasizes that symptom presentation varies based on an individual’s immunity derived from vaccination and previous infection.
It underscores the continued effectiveness of existing vaccines, tests, and treatments against the JN.1 sub-variant.
Prevention and Control Measures
For individuals who are unwell or have had close contact with those exhibiting flu-like symptoms, the advisory recommends the following preventive measures to curb COVID-19 transmission:
- Frequent and thorough hand washing with soap and water; use hand sanitizer if soap and water are unavailable.
- Adherence to respiratory etiquettes by covering mouth and nose while sneezing or coughing, using the elbow.
- Sick individuals are advised to stay at home, rest, and avoid crowded places.
- Implementation of social distancing measures until recovery.
Vaccination as a Crucial Measure
NIH advocates vaccination as the “most effective way” to prevent infection and its severe consequences, especially among high-risk groups.
The advisory underscores that higher antibody levels resulting from complete vaccine doses or booster shots significantly reduce the risk of COVID-19 infection, particularly in vulnerable populations such as the elderly, individuals with comorbidities, and those in high-risk occupational settings.
Enhanced Surveillance Strategies
NIH recommends intensified surveillance for influenza-like illness (ILI) and severe acute respiratory infections (SARI) as a proactive approach for early detection and prompt response in preventing subsequent outbreaks.
Health authorities are directed to send all positive samples for genomic sequencing, enhancing overall monitoring and control efforts.